Κληρονομικότητα
Διομήδης Σπινέλλης
Τμήμα Διοικητικής Επιστήμης και Τεχνολογίας
Οικονομικό Πανεπιστήμιο Αθηνών
dds@aueb.gr
Εισαγωγή
- Συχνά μια σειρά κλάσεων αντικειμένων μπορεί να μοντελοποιηθεί με τη μορφή μιας ιεραρχίας.
- Για παράδειγμα:
- Όλα τα μέλη της Πανεπιστημιακής Κοινότητας είναι
φυσικά πρόσωπα και έχουν ως ιδιότητες το όνομα και το επώνυμό τους.
- Οι φοιτητές έχουν ακόμα ως ιδιότητα τον αριθμό μητρώου τους (id) και το έτος που φοιτούν.
- Όσοι έχουν σχέση εργασίας με το Πανεπιστήμιο έχουν ως ιδιότητα το
μισθό τους.
- Το διοικητικό προσωπικό έχει ως πρόσθετη ιδιότητα τον τομέα ευθύνης του.
- Οι διδάσκοντες έχουν ως πρόσθετη ιδιότητα το τμήμα τους και τα μαθήματα που διδάσκουν.
- Όλα τα μέλη της Πανεπιστημιακής Κοινότητας είναι
φυσικά πρόσωπα και έχουν ως ιδιότητες το όνομα και το επώνυμό τους.
Διάγραμμα κληρονομικότητας
-
Οι σχέσεις των κλάσεων που αναφέραμε μπορούν να παρασταθούν στο παρακάτω
διάγραμμα.
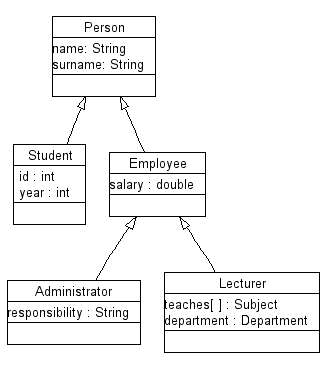
- Κάθε κλάση κληρονομεί τις ιδιότητες της μητρικής της κλάσης.
Κληρονομικότητα σε κλάσεις
- Η ιεραρχία των κλάσεων εκφράζεται στην Java με τον ορισμό μιας κλάσης που είναι υποκλάση (subclass) μιας άλλης κλάσης (που ονομάζεται βασική κλάση (base class)).
- Η σύνταξη για τον ορισμό αυτό είναι της μορφής:
class subclass_name extends base_class_name { // ... } - Κάθε υποκλάση κληρονομεί (inherits) τις μεθόδους και τις ιδιότητες που έχουν οριστεί στη βασική κλάση.
- Η υποκλάση δεν έχει πρόσβαση στις μεθόδους και τις ιδιότητες που έχουν οριστεί ως private στη βασική κλάση.
Υπερφόρτωση
- Η υποκλάση μπορεί να ορίσει νέες ιδιότητες και μεθόδους και να υπερσκελίσει (override) (άλλος όρος: να υπερφορτώσει (override)) ιδιότητες και μεθόδους που έχει ορίσει η βασική κλάση.
- Έτσι, οι περισσότερες κλάσεις αντικαθιστούν τη μέθοδο toString() που επιστρέφει μια συμβολοσειρά που αντιστοιχεί στο περιεχόμενο ενός αντικειμένου και παρέχεται από την Java για όλα τα αντικείμενα με μια πιο εξειδικευμένη μέθοδο.
- Στις μεθόδους αυτές χρησιμοποιούμε την επισημείωση
@Override - Μέσα από την κλάση μπορούμε να αναφερθούμε στις μεθόδους της βασικής της κλάσης με τον προσδιορισμό super.
Παράδειγμα: σχήματα
class Shape {
private int x, y; // Position
public void setPosition(int px, int py) {
x = px;
y = py;
}
@Override public String toString() {
return "Shape(" + x + ", " + y + ")";
}
}
class Circle extends Shape {
private int radius;
public void setRadius(int r) {
radius = r;
}
@Override public String toString() {
return super.toString() + ": Circle(" + radius + ")";
}
}
class Rectangle extends Shape {
private int height, width;
public void setDimensions(int h, int w) {
height = h;
width = w;
}
@Override public String toString() {
return super.toString() + ": Rectangle(" + height + " x " + width + ")";
}
}
class Test1 {
static public void main(String args[])
{
Circle c = new Circle();
Rectangle r = new Rectangle();
r.setPosition(1, 2);
r.setDimensions(50, 50);
c.setPosition(3, 4);
c.setRadius(10);
System.out.println(r);
System.out.println(c);
}
}
Σχήματα: διάγραμμα
-
Ο κώδικας που ορίζει τα σχήματα μπορεί να παρασταθεί σχηματικά ως εξής:
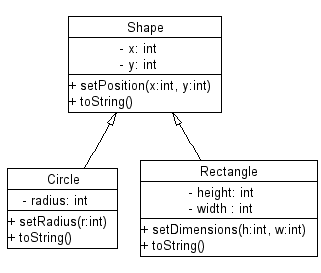
Ο προσδιοριστής protected
- Μπορούμε να ορίσουμε μια κατηγορία μεθόδων και ιδιοτήτων με τον προσδιορισμό protected.
- Αυτές είναι προσβάσιμες από τις υποκλάσεις της κλάσης μας, αλλά όχι από άλλες συναρτήσεις έξω από την ιεραρχία της κλάσης (και του πακέτου).
-
Παράδειγμα:
class Shape { private int x, y; // Position protected int getX() { return x; } protected int getY() { return y; } public void setPosition(int px, int py) { x = px; y = py; } @Override public String toString() { return "Shape(" + x + ", " + y + ")"; } }
Δυναμική διεκπεραίωση
- Μια αναφορά (αντικείμενο) σε μια υποκλάση μπορεί αυτόματα να μετατραπεί σε αναφορά (αντικείμενο) της βασικής της κλάσης.
- Αυτό επιτρέπεται διότι κάθε αντικείμενο μιας υποκλάσης είναι (is a) και αντικείμενο της βασικής κλάσης.
- Το αντικείμενο συνεχίζει να διατηρεί τις ιδιότητες της υποκλάσης μετά τη μετατροπή και μπορεί να μετατραπεί πίσω στην ίδια υποκλάση με τη χρήση ρητού τελεστή μετατροπής (cast).
Παράδειγμα δυναμικής διεκπεραίωσης
static public void main(String args[])
{
Rectangle r = new Rectangle();
Shape s;
r.setPosition(1, 2);
r.setDimensions(50, 50);
s = r;
s.setPosition(10, 20);
System.out.println(r);
System.out.println(s);
r = (Rectangle)s;
}
Λειτουργία δυναμικής διεκπεραίωσης
- Οι υποκλάσεις μιας κλάσης μπορούν να αντικαταστήσουν μια μέθοδό της με μια που θα ορίσουν αυτές.
- Όταν κληθεί η μέθοδος που έχει αντικατασταθεί από μια υποκλάση μέσω ενός αντικειμένου της βασικής κλάσης το οποίο έχει προέλθει από αντικείμενο κάποιας υποκλάσης τότε θα κληθεί η αντίστοιχη μέθοδος της υποκλάσης από την οποία έχει προέλθει το αντικείμενο.
Πλεονεκτήματα της δυναμικής διεκπεραίωσης
- Η δυνατότητα της
δυναμικής διεκπεραίωσης (dynamic dispatch) επιτρέπει:
- το δυναμικό καθορισμό της συμπεριφοράς ενός αντικειμένου ανάλογα με την κλάση του κατά την εκτέλεση του προγράμματος,
- την αλλαγή της συμπεριφοράς μιας παλιάς κλάσης από μια νεώτερη (υποκλάση της) και
- την ενοποιημένη διαχείριση διαφορετικών αντικειμένων μέσω της βασικής τους κλάσης.
- Η δυνατότητα αυτή προάγει τη Java από γλώσσα που υποστηρίζει τα αντικείμενα σε αντικειμενοστρεφή γλώσσα.
Σφραγισμένες κλάσεις
Με τους προσδιοριστέςsealed και permits
μπορούμε να
ορίσουμε ποιες κλάσεις επιτρέπεται να επεκτείνουν τη μητρική κλάση.
public sealed class Shape permits Circle, Rectangle {
}
class Circle extends Shape {
}
class Rectangle extends Shape {
}
Αφηρημένες κλάσεις
- Αν μια μέθοδος μιας κλάσης οριστεί με τον προσδιοριστή abstract
και χωρίς σώμα τότε η συνάρτηση αυτή είναι
ιδεατή (abstract) δηλαδή δεν έχει υλοποίηση στη
συγκεκριμένη κλάση.
Παράδειγμα:
abstract class Document { public abstract String identify(); } - Αν μια κλάση περιέχει (ή έχει κληρονομήσει) τουλάχιστον μια ιδεατή μέθοδο τότε και αυτή πρέπει να οριστεί με τον προσδιοριστή abstract και ονομάζεται ιδεατή (abstract).
- Σε μεταβλητές τύπου μιας ιδεατής κλάσης μπορούν να ανατεθούν αντικείμενα από μη ιδεατές υποκλάσεις της. Τα ίδια όμως τα αντικείμενα μιας ιδεατής κλάσης δεν μπορούν ποτέ να δημιουργηθούν αυτούσια.
Σχεδιάζοντας με αφηρημένες κλάσεις
- Οι ιδεατές κλάσεις χρησιμοποιούνται μόνο για να ορίσουν γενικές έννοιες από τις οποίες εκπορεύονται συγκεκριμένες κλάσεις.
- Παράδειγμα: ένα σχέδιο του πληροφοριακού συστήματος του Πανεπιστημίου μπορεί να ορίσει την ιδεατή κλάση person ως βασική κλάση για τις υποκλάσεις student, employee και visitor. Αν και δε θα μπορεί να δημιουργηθεί ένα νέο αντικείμενο με βάση την αφηρημένη κλάση person, αυτή μπορεί να περιέχει ορισμένα βασικά χαρακτηριστικά όπως birth_date και να επιβάλει την υλοποίηση συγκεκριμένων μεθόδων όπως home_page_URL() ορίζοντάς τις ως ιδεατές.
Παράδειγμα: σχήματα
- Το παράδειγμα ορίζει τη βασική κλάση Shape και τις υποκλάσεις της Circle και Rectangle.
- Η μέθοδος area μπορεί να οριστεί για τις υποκλάσεις και κατά την εκτέλεση του προγράμματος να εκτελεστεί η σωστή έκδοσή της.
- Η συνάρτηση toString της Shape εκμεταλλεύεται τη δυνατότητα αυτή και μπορεί να κληθεί (και να δουλέψει σωστά) με όρισμα οποιαδήποτε από τις υποκλάσεις της shape.
Σχήματα: ο κώδικας
abstract class Shape {
private double x, y; // Position
protected double getX() { return x; }
protected double getY() { return y; }
public void setposition(double px, double py) {
x = px;
y = py;
}
public abstract double area();
@Override public String toString() {
return "Shape(x=" + x + ", y=" + y + ", area=" + area() + ")";
}
}
class Circle extends Shape {
private double radius;
public void setradius(double r) {
radius = r;
}
@Override public double area() {
return Math.PI * radius * radius;
}
@Override public String toString() {
return super.toString() + ": Circle(" + radius + ")";
}
}
class Rectangle extends Shape {
private double height, width;
public void setdimensions(double h, double w) {
height = h;
width = w;
}
@Override public double area() {
return height * width;
}
@Override public String toString() {
return super.toString() + ": Rectangle(" + height + " x " + width + ")";
}
}
class Test2 {
static public void main(String args[])
{
Circle c = new Circle();
Rectangle r = new Rectangle();
Shape s[] = new Shape[2];
s[0] = r;
r.setposition(1, 2);
r.setdimensions(50, 50);
s[1] = c;
c.setposition(3, 4);
c.setradius(10);
for (int i = 0; i < s.length; i++)
System.out.println(s[i]);
}
}
Shape(x=1.0, y=2.0, area=2500.0): Rectangle(50.0 x 50.0) Shape(x=3.0, y=4.0, area=628.3185307179587): Circle(10.0)
Τελικές μεταβλητές
- Συχνά στο πρόγραμμά μας χρησιμοποιούμε αριθμητικές ή άλλες σταθερές (constants).
- Αν οι σταθερές εμφανίζονται μέσα στον κώδικα αυτό τον κάνει
δυσνόητο και δύσκολο να συντηρηθεί.
double area = 6 * length * width; - Με τον προσδιοριστή final μπορούμε να ορίσουμε μεταβλητές των οποίων
η τιμή δε θα αλλάξει κατά τη διάρκεια εκτέλεσης του προγράμματος.
final int CUBE_FACETS = 6; double area = CUBE_FACETS * length * width; - Οι αριθμητικές σταθερές τυπικά ονομάζονται με κεφαλαία γράμματα.
Τελικά ορίσματα
- Με
finalορίζουμε ακόμα ορίσματα που δεν μεταβάλλονται μέσα σε μια μέθοδο.static double square(final double d) { return d * d; } - Προσοχή: η λέξη final ορίζει ότι μένει σταθερή μια μεταβλητή όχι αμετάβλητο (immutable) το αντίστοιχο αντικείμενο.
Τελικά πεδία
- Με
finalορίζουμε ακόμα πεδία που δεν μεταβάλλονται μέσα στην κλάση. - Τα πεδία αυτά πρέπει να αρχικοποιηθούν είτε στον ορισμό τους είτε σε όλους τους κατασκευαστές.
- Μετά την αρχικοποίηση δεν επιτρέπεται να αλλάξουν τιμή.
class FixedPlanarCoordinate {
final int x, y;
final int z = 0;
FixedPlanarCoordinate(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
public int getX() {
return x;
}
public int getY() {
return y;
}
public int getZ() {
return z;
}
}
Δημόσιες τελικές μεταβλητές
Μια κλάση μπορεί να ορίσει δημόσιες σταθερές ιδιότητες ως μέλη για να μπορούν να χρησιμοποιηθούν από άλλες κλάσεις.
class PhysicalConstants {
// Speed of light in vacuum (m/s)
public static final double c = 299792458;
// Permeability of vaccum (N/A/A)
public static final double mu0 = 4 * Math.PI * 10e-7;
// Newtonian constant of gravitation (m*m*m/kg/s/s)
public static final double G = 6.67259e-11;
// Planck constant (J*s)
public static final double h = 6.6260755e-34;
// Elementary charge (C)
public static final double e = 1.60217733e-19;
}
Τελικές κλάσεις και μέθοδοι
- Με τον προδιοριστή final μπορούμε να περιορίσουμε τη χρήση κληρονομικότητας σε κλάσεις και μεθόδους.
- Μια κλάση με τον προσδιοριστή final δεν μπορεί να επεκταθεί.
final class PasswordChecker { // Class contents here } - Μια μέθοδος με τον προσδιοριστή final δεν μπορεί να αντικατασταθεί
σε μια υποκλάση.
class Password { final boolean isPasswordValid() { /* ... */ } } - Καλό είναι να θέτουμε τον προσδιοριστή αυτό σε μεθόδους που δεν έχουν σχεδιαστεί για αντικατάσταση (π.χ. μέσω αφηρημένης κλάσης ή διεπαφής).
Τελικές κλάσεις και μέθοδοι στην πράξη
- Με τελικές κλάσεις και μεθόδους μπορούμε να είμαστε σίγουροι πως μια συγκεκριμένη υλοποίηση στην οποία βασίζεται το πρόγραμμά μας δε θα αλλάξει από άλλες κλάσεις.
- Τελικές κλάσεις και μεταβλητές επιτρέπουν στο μεταγλωττιστή να πραγματοποιήσει και ορισμένες βελτιστοποιήσεις στον παραγώμενο κώδικα.
- Η απόφαση όμως για τη χρήση του προσδιοριστή πρέπει να βασίζεται αποκλειστικά στο σχεδιασμό του προγράμματος.
Η ιεραρχία κλάσεων στη βιβλιοθήκη της Java
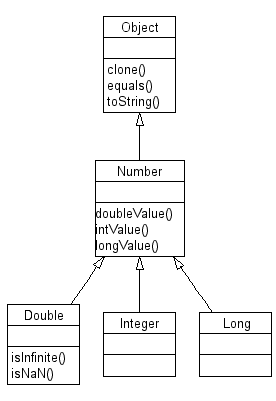
- Όλες οι κλάσεις της Java έχουν ως βασική κλάση την κλάση Object
- Η βιβλιοθήκη της Java χρησιμοποιεί την κληρονομικότητα για να οργανώσει την ιεραρχία των κλάσεων που υποστηρίζει.
Java: παράσταση αριθμών-number
Java: κλάσεις για το σχηματισμό μηνυμάτων
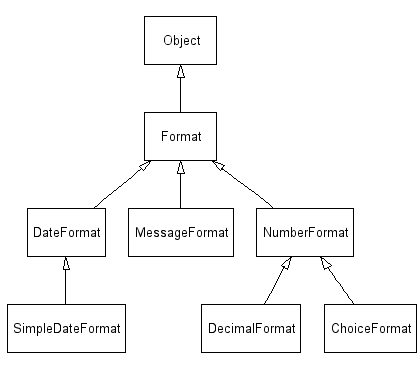
Παράδειγμα χρήσης μηνυμάτων
Object[] arguments = {
Integer.valueOf(7),
new Date(System.currentTimeMillis()),
"a disturbance in the Force"
};
String result = MessageFormat.format(
"At {1,time} on {1,date}, there was {2} on planet {0,number,integer}.",
arguments);
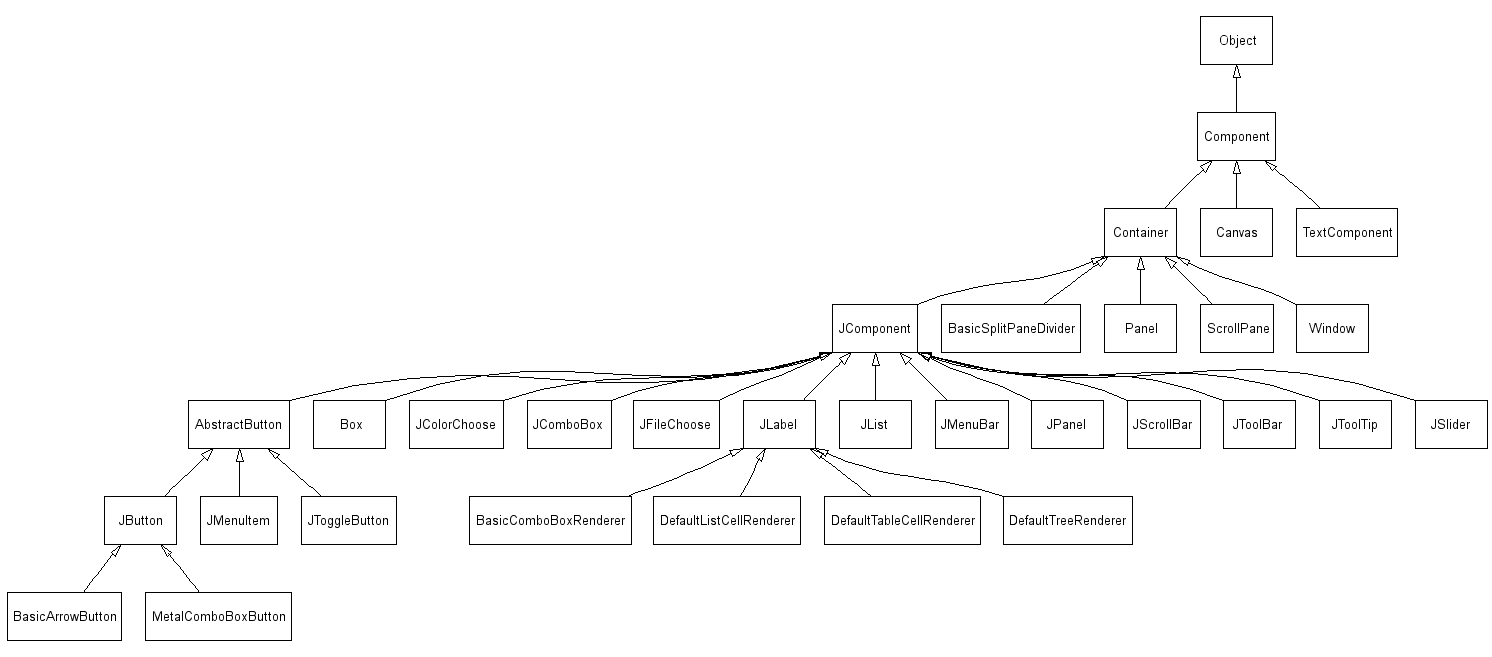
Java: Τμήμα της ιεραρχίας Swing
Java: Τεκμηρίωση των κλάσεων
Εδώ (https://docs.oracle.com/en/java/javase/21/docs/api/index.html) μπορείτε να δείτε την τεκμηρίωση όλων των κλάσεων που προσφέρει η Java.
Κάθε κλάση τεκμηριώνει:- Τη θέση της στην ιεραρχία
- Γνωστές υποκλάσεις
- Ιδιότητες
- Κατασκευαστές
- Μεθόδους
- Κληρονομούμενες μεθόδους ανά μητρική κλάση
Άσκηση: κληρονομικότητα
Άσκηση 5
Μπορείτε να κατεβάσετε το αντίστοιχο αρχείο και να στείλετε τους βαθμούς σας από τους δεσμούς που βρίσκονται στη σελίδα των ασκήσεων.Βιβλιογραφία
- Joyce Farrell. Java: Εκμάθηση με πρακτικά παραδείγματα. 2η έκδοση. Εκδόσεις Κριτική, Αθήνα 2024. Κεφ. 9.
- Rogers CadenheadΠλήρες εγχειρίδιο της Java 12Όγδοη έκδοση. Εκδόσεις Μ. Γκιούρδας, Αθήνα 2023. Κεφ. 5.
- Rogers CadenheadΠλήρες εγχειρίδιο της Java 12Όγδοη έκδοση. Εκδόσεις Μ. Γκιούρδας, Αθήνα 2023. Κεφ. 5.
- Herbert Schildt. Οδηγός της Java 7. 5η έκδοση. Εκδόσεις Γκιούρδας Μ., Αθήνα 2012. Κεφ. 7.
- Harvey M. Deitel και Paul J. Deitel. Java Προγραμματισμός, 6η έκδοση. Εκδόσεις Μ. Γκιούρδας, Αθήνα 2005. Κεφάλαια 9, 10.
- Else Lervik και Vegard B. Havdal Java με UML. Εκδόσεις Κλειδάριθμος 2005. Κεφάλαιο 12.
- Γιώργος Λιακέας Εισαγωγή στην Java. σ. 141-152 Εκδόσεις Κλειδάριθμος 2001.
- Γιάννη Κάβουρα. Προγραμματισμός με Java. Εκδόσεις Κλειθάριθμος, Αθήνα 2003. Κεφάλαιο 13.
- Rogers Cadenhead και Laura Lemay Πλήρες εγχειρίδιο της Java 2 Εκδόσεις Μ. Γκιούρδας, Αθήνα 2003. σ. 25-31